MRCP, magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography, is special kind of MRI where pictures are obtained of the pancreatic and bile ducts. MRI machines use radio waves and magnets to scan internal organs and tissues. An MRCP does not use contrast but if it is combined with an MRI, you may be given contrast. A contrast dye is usually injected in your veins to help so the images are clearly defined to help aid in the diagnosis. Unexplained abdominal pain and jaundice often the most common diagnosis.
What does an MRCP help diagnose?
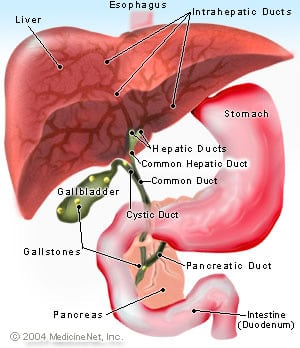
An MRCP is a non-invasive test that can help diagnose gallstones, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, blocked pancreatic or bile ducts, bile ducts stones or cysts, bile duct cancer and pancreatic cancer. MRCP is also used to treat PSC. PSC (primary sclerosingcholangitis), is a disease that damages and blocks bile ducts inside and outside the liver. Bile is a liquid made in the liver. Bile ducts are tubes that carry bile out of the liver to the gallbladder and small intestine. In the intestine, bile helps break down fat in food.
What is the difference between and MRCP and ERCP?
- MRCP is noninvasive while an ERCP is invasive, meaning it requires a cut or incision.
- MRCP uses radio frequency waves while an ERCP uses x-rays, which uses radiation.
References
Cleveland Clinic. 2022. MRCP. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/24457-magnetic-resonance-cholangiopancreatography-mrcp
Cancer Center. 2022. MRCP. https://www.cancercenter.com/diagnosing-cancer/diagnostic-imaging/mrcp


