Barium Swallow, also known as videofluoroscpoic swallow study, tests your ability to swallow and may be used to determine the cause of painful swallowing, difficulty with swallowing, abdominal pain, bloodstained vomit, or unexplained weight loss.
Barium sulfate is a metallic compound that shows up on X-rays and is used to help see abnormalities in the esophagus and stomach. When taking the test, you drink a preparation containing this solution. The X-rays track its path through your digestive system.
Problems that can be detected with a barium swallow: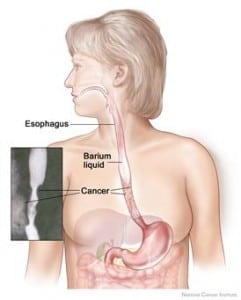
- Narrowing or irritation of the esophagus (for example, Schatski’s ring)
- Disorders of swallowing (dysphagia – difficulty swallowing), spasms of the esophagus or pharynx
- Hiatal hernia (an internal defect that causes the stomach to slide partially into the chest)
- Abnormally enlarged veins in the esophagus (varices) that cause bleeding
- Ulcers
- Tumors
- Polyps (growths that are usually not cancerous, but develop into cancer)
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
This test may be ordered if you have problems swallowing and are at risk of choking or aspiration (food or liquid going into the lungs). It is also needed if you have a feeding tube and the doctor wants to check if you are ready to return to eating by mouth.
During the test, you are given tiny amounts of food and liquids of different textures to swallow, containing a small amount of barium that shows up clearly on x-rays. You are observed carefully for signs of problems as each food or liquid is swallowed. If problems occur as you are swallowing, steps are quickly taken for treatment.
Risks and possible complications of Barium Swallow
A barium swallow is generally a safe test, but like any procedure, there are occasionally complications. Your doctor should be advised of problems so you can be treated right away. The following are some of these complications:
- Aspiration – accidentally get barium into the trachea (windpipe)
- Constipation
- Radiation exposure from x-rays
- Blockage (obstruction) of the bowel due to retained barium allergic reaction to the barium
Helpful Links

